Why do we need wood drying?
There is a certain amount of moisture in the wood. The amount of moisture in the wood varies with the species of tree, the age of the tree, and when the tree was cut. In order to ensure the quality of the finished wood products and increase the service life of the wood, corresponding measures need to be taken to reduce the moisture (moisture content) in the wood. If you want to reduce the moisture of the wood, you should increase the temperature of the wood, so that the moisture in the wood moves outward and evaporates, and in the air with a certain flow speed, the moisture quickly leaves the wood, so as to achieve the purpose of drying.
Wood drying can improve wood quality, effectively prevent the decline of wood grade, and increase the efficiency of wood utilization. At the same time, the process of wood drying is also the most energy-intensive in the woodworking production process.
Therefore, the goal of wood drying is to achieve the goal of speeding up and save energy on the premise of ensuring high-quality drying.

Drying kiln type
Commonly used artificial wood drying methods that have achieved large-scale industrialization so far include traditional drying, high-temperature drying, dehumidification drying, solar drying, vacuum drying, flue gas drying, high-frequency vacuum drying, etc.
Traditional wood drying
The traditional drying method uses humid air under normal pressure as the drying medium, steam, hot water, furnace gas, or hot oil as the heat supply source to indirectly heat the air, and the temperature of the drying medium (humid air) is below 100 °C.

High-temperature drying
The temperature of the drying medium in the high-temperature drying method is above 100 °C, and this type of drying medium is generally dominated by atmospheric pressure superheated steam.
Flue gas drying
The flue gas drying method is equipped with a combustion furnace for burning wood waste (or other fuels), and the flue gas generated by the combustion is used as a heat source. Flue gas drying is the preliminary stage of furnace gas drying, which generally refers to a simple drying kiln, which is directly or indirectly heated by the flue gas generated after burning wood waste to achieve the effect of drying wood.

Dehumidification drying
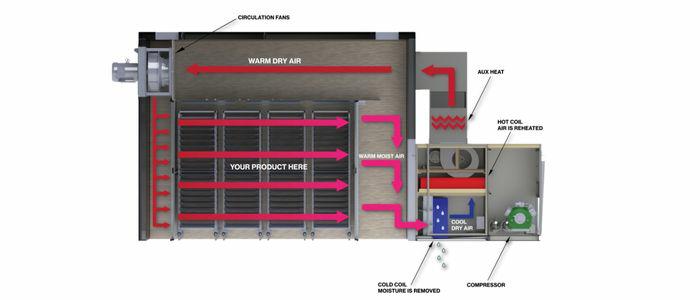
The dehumidification drying method (also known as heat pump drying) is the same as the drying medium (humid air) of the traditional drying method. The difference between them is that traditional drying adopts the method of open circulating air, and regularly discharges a part of the hot air with relatively high humidity from the drying kiln At the same time, the same amount of cold air is sucked in, so the traditional drying ventilation heat loss is large.
During dehumidification and drying, the humid air passes through the refrigeration system of the dehumidifier and then returns to the drying kiln through cooling and dehumidification heating to carry out a closed circulation of air. The heat generated and released when the humid air is dehumidified depends on the recovery of the refrigeration system to reheat the air, so the energy-saving effect of dehumidification and drying is more obvious than that of traditional drying.
Solar drying
Solar drying usually uses the heat generated by the sun to directly heat the air, relying on fans to circulate the air between the solar collector and the dried wood.
Generally, there are two types of greenhouse type and collector type. The former integrates the collector and the drying kiln. The latter separates the collector and the drying chamber, so the latter has a larger volume than the greenhouse type and is relatively convenient to place.
Due to the limitation of climate and weather, solar drying needs to be combined with furnace gas, steam, heat pump, etc. to form a combined drying device.

High-frequency vacuum and the Vacuum drying
Both the high-frequency vacuum method and the vacuum drying method use wet wood as the dielectric. Under the action of the alternating electromagnetic field, the water molecules in the dried wood rotate at a very high frequency, and friction occurs between the water molecules to generate heat, making the wood from the inside to the outside. Simultaneously heat and dry.
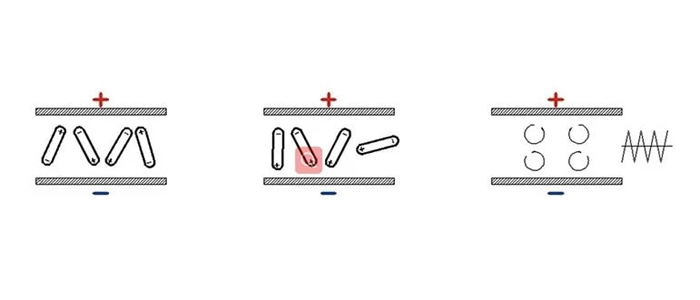
These two drying methods are characterized by fast drying speed, uniform heating of wood and better drying quality. The difference between high frequency and vacuum drying is that the former has a low frequency, a longer wavelength, and deeper penetration into the wood. The frequency of vacuum drying is higher than that of vacuum high frequency (also known as ultra-high frequency), But the wavelength is shorter, and its drying rate It is larger than the high frequency, but the penetration depth of the wave is less than that of the high frequency.
When the wood is dried in a high-frequency vacuum, The difference in water vapor pressure inside and outside the wood increases, which accelerates the speed of moisture migration in the wood. At the same time, due to the low boiling point of water in the vacuum state, it can be dried at a lower temperature (such as about 70°C). A high drying rate can be achieved under the condition of high frequency vacuum, so the high frequency vacuum has the characteristics of a short drying cycle, small drying stress, and good drying quality.

Advantages of drying wood:
- Improve the service life of wood and wood products.
When wood is exposed to the air for a long time, it will suffer from moisture and dry shrinkage. This situation often leads to wood cracking and deformation, affecting the use of wood and causing waste.If wood products (such as floors, windows, furniture, doors, etc.) are made of wet wood or wood that has not been dried, it looks good when it is first made, but after a period of time, it will occur as the wood naturally dries. The door frame is skewed, the floor is warped, the tenon is loosened or the wood board is cracked, etc., resulting in irreparable losses.

If the wood product is dried to the corresponding moisture content before use, the stability of the wood product structure can be ensured, and the finished product can be more durable.

- The strength of wood and wood products can be greatly improved.
When the moisture content of the wood is low to a certain value, the strength of the wood will increase as the moisture content of the wood decreases. After drying, the wood can be favorable for cutting conditions and improve the strength, bonding strength and surface quality of wood products.
The thermal and electrical conductivity of wood decreases with decreasing moisture content. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity by reducing the moisture content to improve the thermal insulation and thermal insulation properties of wood.

- Improve the quality and corrosion resistance of wood.
Wet wood tends to rot or be attacked by insects if exposed to the air for extended periods of time without proper precautions. When the moisture content of wood is reduced to below 20%, it can be greatly corroded and damaged by pests. Therefore, before the production of wood products, the wood will be dried to a moisture content of 8-12%. This can ensure the strength of the wood, but also improve the corrosion resistance of the wood.
- Effectively reduce the weight of wood.
The moisture content of newly felled wood even exceeds the weight of the wood itself. After a short period of storage and natural drying, its moisture content is still high. After the wood is kiln dried, its weight can be reduced by about 30-50%, which is beneficial to improve the transportation capacity of vehicles. In short, the dried wood can not only ensure the quality of wood products, enhance the efficiency of wood use, and prolong the use time, so as to achieve the purpose of saving wood.
Years of practice have the data show that wood drying is an indispensable condition in the production of wood products.




